From my Forbes.com blog The New Persuaders:
Just in time for prime gift-giving holidays like Friday’s World Rabies Day (or if you prefer, Ask A Stupid Question Day), Facebook today launched a social gift service. It’s rolling out to only a select few for now.
I must be one of them, because I was able to send something to my wife to try it out. But in its current form, I doubt I’m going to use it much.
This isn’t the 2.0 version of the Facebook Gifts virtual-gift service that the company shut down two years ago, by the way. In fact, the new Gifts is built upon, and run by, the folks at Karma, the gift-giving service Facebook acquired in May.
It actually looks pretty good. And while I have ordered precisely one gift that obviously has not yet been delivered, so I can’t judge the entire gift-giving process, it worked quite smoothly. I clicked on my wife’s Timeline, clicked the gift button, and off I went to order her some caramels. She can even pick her own flavor–that’s pretty cool.
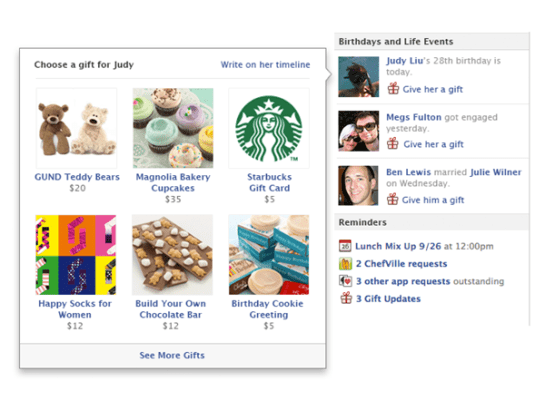 In this case, I obviously know her address, so one advantage of Facebook Gifts–not having to know or ask for someone’s address–is moot in my case. What’s more, I didn’t get an automatic reminder I might get if it were her birthday, so that bit of friction elimination wasn’t a factor for me either. But it’s fast and easy to send gifts to friends, and that’s great–not just for consumers, but for Facebook, which can use a service that brings in revenues not dependent upon its brand of advertising that many large marketers are still doubtful about.
In this case, I obviously know her address, so one advantage of Facebook Gifts–not having to know or ask for someone’s address–is moot in my case. What’s more, I didn’t get an automatic reminder I might get if it were her birthday, so that bit of friction elimination wasn’t a factor for me either. But it’s fast and easy to send gifts to friends, and that’s great–not just for consumers, but for Facebook, which can use a service that brings in revenues not dependent upon its brand of advertising that many large marketers are still doubtful about.
So what isn’t great, at least for me?
* A lot of the most prominent gifts are pretty vanilla–teddy bears, spa appointments, flowers, cupcakes. Maybe they’re fine products. Maybe they’re the sort of thing most people give their friends. But for a service with a tagline “real friends, real gifts,” too many of these products seem just too impersonal. Products, especially gifts, are not necessarily fungible, and all the less so for close friends for whom you’re supposed to be getting something special. And if they’re not close friends–and let’s be honest, most people don’t have several hundred close friends–I probably won’t be sending them many gifts, from Facebook or anywhere else. …






